A research paper lead by Jeremy Harrison of the atmospheric composition group has been highlighted as an ACP research highlight.
The vast majority of emissions of fluorine-containing molecules are anthropogenic in nature, e.g. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). Many of these fluorine-containing species deplete stratospheric ozone and are regulated by the Montreal Protocol. Once in the atmosphere they slowly degrade, ultimately leading to the formation of hydrogen fluoride (HF), the dominant reservoir of stratospheric fluorine due to its extreme stability. Monitoring the growth of stratospheric HF is therefore an important marker for the success of the Montreal Protocol.
We report the comparison of global distributions and trends of HF measured in the Earth’s atmosphere by the satellite remote-sensing instruments ACE-FTS (Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment Fourier transform spectrometer), which has been recording atmospheric spectra since 2004, and HALOE (HALogen Occultation Experiment), which recorded atmospheric spectra between 1991 and 2005, with the output of SLIMCAT, a state-of-the-art three-dimensional chemical transport model. In general the agreement between observation and model is good, although the ACE-FTS measurements are biased high by ∼ 10 % relative to HALOE. The observed global HF trends reveal a substantial slowing down in the rate of increase of HF since the 1990s: 4.97 ± 0.12 % year−1 (1991–1997; HALOE), 1.12 ± 0.08 % year−1 (1998–2005; HALOE), and 0.52 ± 0.03 % year−1 (2004–2012; ACE-FTS). In comparison, SLIMCAT calculates trends of 4.01, 1.10, and 0.48 % year−1, respectively, for the same periods; the agreement is very good for all but the earlier of the two HALOE periods. Furthermore, the observations reveal variations in the HF trends with latitude and altitude; for example, between 2004 and 2012 HF actually decreased in the Southern Hemisphere below ∼ 35 km. An additional SLIMCAT simulation with repeating meteorology for the year 2000 produces much cleaner trends in HF with minimal variations with latitude and altitude. Therefore, the variations with latitude and altitude in the observed HF trends are due to variability in stratospheric dynamics on the timescale of a few years. Overall, the agreement between observation and model points towards the ongoing success of the Montreal Protocol and the usefulness of HF as a metric for stratospheric fluorine.
The full paper can be found here: http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/16/10501/2016/acp-16-10501-2016.html
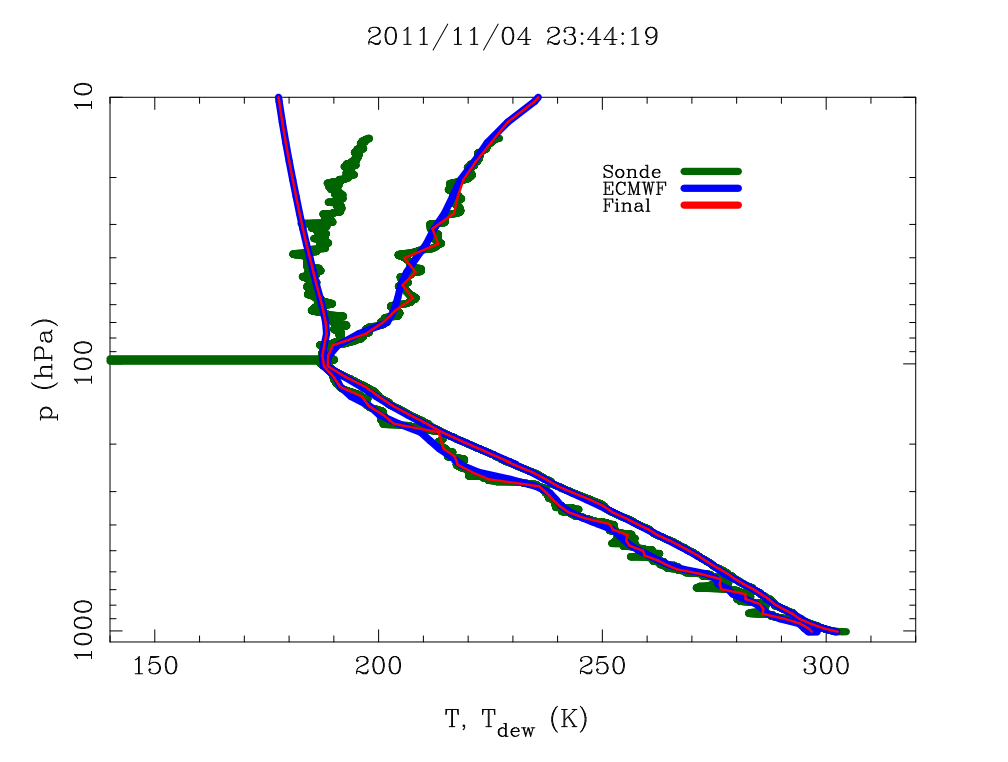 Radiosonde soundings from the GRUAN data record are shown to be consistent with IASI measured radiances via the LBLRTM radiative transfer model in the part of the spectrum that is mostly affected by water vapour absorption in the upper troposphere (from 700 hPa up). This result is key to have consistency between radiosonde and satellite measurements for climate data records, since GRUAN, IASI and LBLRTM constitute reference measurements in each of their fields. This is specially the case for night time radiosonde measurements. Although the sample size is small (16 cases), day time GRUAN radiosonde measurements seem to have a small dry bias of 2.5 % in absolute terms of relative humidity, located mainly in the upper troposphere, with respect to LBLRTM and IASI.
Radiosonde soundings from the GRUAN data record are shown to be consistent with IASI measured radiances via the LBLRTM radiative transfer model in the part of the spectrum that is mostly affected by water vapour absorption in the upper troposphere (from 700 hPa up). This result is key to have consistency between radiosonde and satellite measurements for climate data records, since GRUAN, IASI and LBLRTM constitute reference measurements in each of their fields. This is specially the case for night time radiosonde measurements. Although the sample size is small (16 cases), day time GRUAN radiosonde measurements seem to have a small dry bias of 2.5 % in absolute terms of relative humidity, located mainly in the upper troposphere, with respect to LBLRTM and IASI.